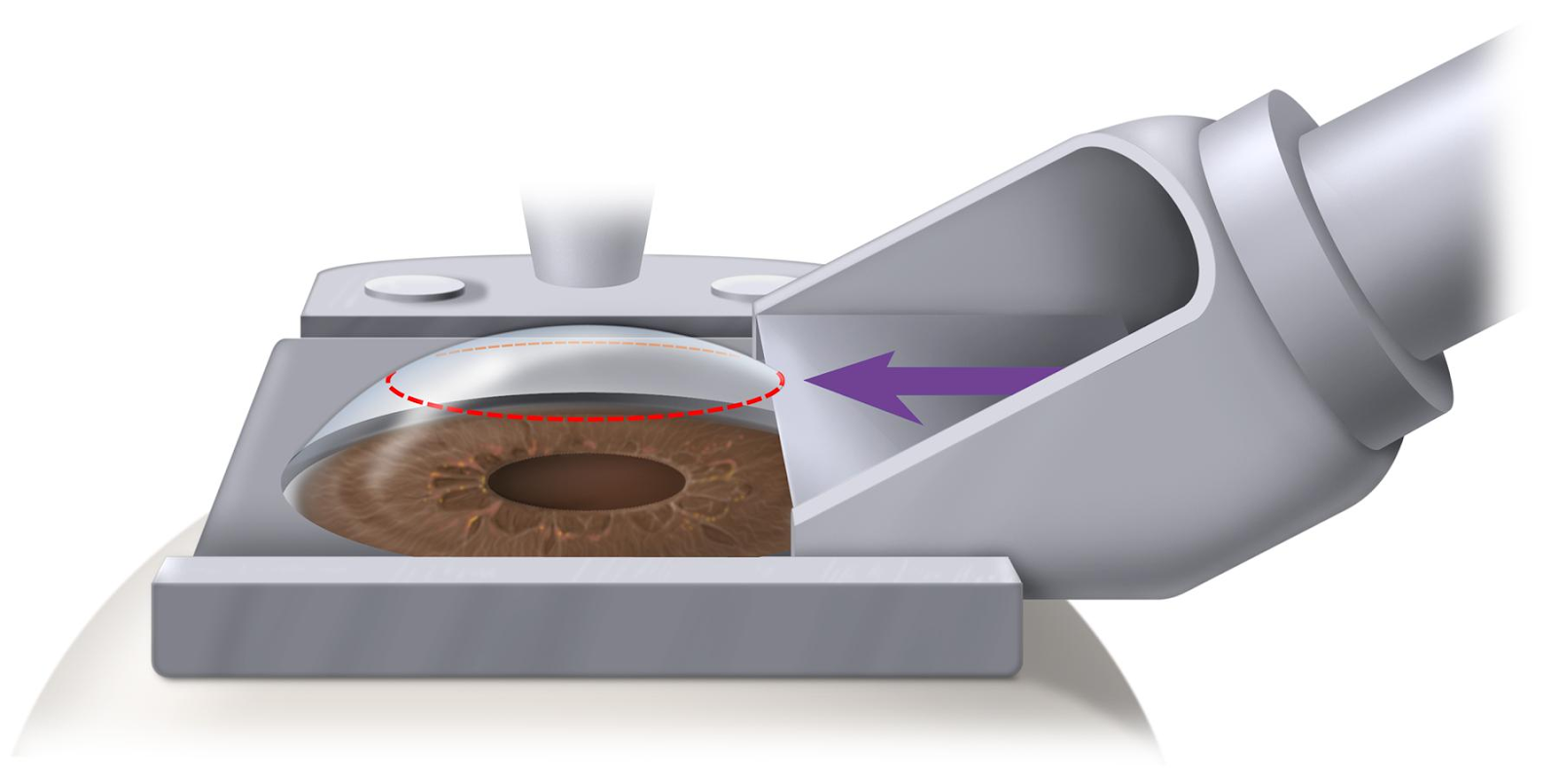
LASIK laser eye surgery involves creating and reflecting a thin flap of the superficial cornea, revealing a central portion of the deeper cornea. An excimer laser is used to remove corneal tissue from the deeper surface in the center area. After which the flap is replaced and allowed to heal naturally.
Lasik laser eye treatment or laser vision correction is meant for candidates who have blurred vision or other eye defects. These people do not want to use glasses or contact lenses for the rest of their lives, hence they opt to undergo LASIK surgery.
Brief description of Lasik laser eye surgery procedures
The area is cleansed and sterilized after a drop of anesthesia is instilled. A clip holds the eyelids open to allow access. A ring is used to support the eye so that the flap can be created. A thin layer of superficial cornea forms the flap.
The flap is hinged at one edge so it can be gently mirrored. The excimer laser is then used to restructure the exposed layer of the cornea (very similar to PRK). The flap is then adjusted and reattached. Because the front surface has been replaced, vision returns quickly, usually returning one day.
Limitations
If the corneal thickness is appropriate, excellent outcomes in the +4 to -10 diopter range can be predicted. After laser ablation, sufficient cornea thickness must be left deep into the flap. This may limit the treatment range and damage the optical zone, particularly in thinner corneas with higher corrections. Because the corneal flap does not become entirely secure for 4 weeks, there are some restrictions on your activities during that time. You can also read about What Should I Avoid Following Laser eye surgery, LASIK? by clicking here.
Is it possible to have LASIK with astigmatism?
Definition of Astigmatism
Refractive errors are a class of phenomena that impact how light bends or refracts as it enters the eye. Astigmatisms, like hyperopia, myopia, and presbyopia, is a typical refractive defects. Astigmatism is typically present at birth due to the shape of the eye. It can, however, change with time.
The cornea, the transparent tissue at the front of the eye, is the most prevalent cause of astigmatism. This is known as cornea astigmatism. The crystalline lens can also cause astigmatism within the eye. This is referred to as lenticular astigmatism.
The cornea’s curvature is uneven in corneal astigmatism rather than being curved like a perfect sphere. The astigmatic corneal shape is more like a football than a basketball or soccer ball. Similarly, with lenticular astigmatism, the shape of the lens is irregular.
When the cornea or lens is asymmetric, light passing through the eye divides and forms two distinct focal points. Depending on whether you also have myopia or hyperopia, the two focal points strike the retina in front of (myopia) or behind (hyperopia). The retina is the rear of the eye’s sensory tissue. People with astigmatism have hazy vision when light does not focus properly.

Astigmatism Treatment
You’re probably wondering if you can have LASIK if you have astigmatism. Yes, but it will also be subject to on the degree of your astigmatism and whether it is symmetric or asymmetric.
Is LASIK Eye Surgery Effective for Astigmatism?
You may have learned that LASIK and astigmatism do not mix; however, this is not true. The laser repairs astigmatism in LASIK eye surgery by making the cornea more symmetrical. When astigmatism is corrected, vision improves.
So, does LASIK help with astigmatism? Usually, the answer is yes. As long as the astigmatism is of the proper type and falls within the treatment restrictions, LASIK is effective in treating most people’s astigmatism.
Are there certain types of astigmatism that LASIK cannot correct?
Because LASIK only treats the cornea, it can only fix corneal astigmatism. Lenticular astigmatism will not be impacted.
Astigmatism is classified into two types: regular and irregular. The form of astigmatism discussed thus far in this text is the most prevalent regular subtype. Trauma to the eye or certain corneal disorders such as keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration, epithelial basement membrane dystrophy, and others can cause irregular astigmatism. Irregular astigmatism is more challenging to treat with refractive surgery, and LASIK is typically not an option.
The treatment parameters for LASIK are relatively generous. Thus, even severe astigmatism may be accommodated. With severe astigmatism, Doctors must assess whether surgery is still a safe and effective treatment choice.
Are you thinking about getting LASIK? Find out more about this laser eye surgery
Before deciding to have LASIK, be sure you’re a good candidate, understand the benefits and potential risks, and have realistic expectations about your vision after surgery and for years to come. Be a well-prepared and informed patient by examining the materials below before having LASIK to achieve the best possible outcome. If any of these materials raise any concerns for you, be careful to discuss them with your ophthalmologist.
How long does healing take following laser eye surgery?
One advantage of using laser surgery to treat refractive problems is that recovery time is usually short.
Your eye begins to heal immediately after LASIK, LASEK, or other similar treatments that generate a replacement flap in your cornea. Your eye surgeon or another eye specialist will test your eyesight and ensure your eyes are properly healing the day after surgery. In most circumstances, you can return to work and drive the next day.
Healing may take a little longer if you have had PRK. This is due to removing a thin outer layer of corneal cells (rather than replaced as a flap-like with LASIK or LASEK). The cells regenerate; however, it takes a few days following surgery. This will increase the time it takes to return to work and drive comfortably and safely.
Having some hazy vision or seeing your eyesight altering for several weeks or even months after laser eye surgery is normal. You may also experience dry eyes, glare, or halos around lights.
You will most likely be booked for regular follow-up visits with your eye doctor for six months or longer after laser surgery to check on how your eyes are doing. Most patients’ vision is steady and clear six months after surgery. If you have dry eyes or other visual abnormalities following surgery, you should notice that most of these symptoms have gone away or have become considerably less noticeable.
If you still have vision problems six months following laser eye surgery, your ophthalmologist may propose another laser surgery operation called an enhancement to fine-tune your eyesight.